Summary of product characteristics
This medicinal product is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions. See section 4.8 for how to report adverse reactions
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Terrosa 20 micrograms/80 microliters solution for injection
2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
Each dose of 80 microliters contains 20 micrograms of teriparatide*.
One cartridge of 2.4 mL of solution contains 600 micrograms of teriparatide (corresponding to 250 micrograms per mL).
*Teriparatide, rhPTH(1-34), produced in E. coli, using recombinant DNA technology, is identical to the 34-N-terminal amino acid sequence of endogenous human parathyroid hormone.
For the full list of excipients, see section 6.1.
3. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM
Solution for injection. Colourless, clear solution for injection with a pH of 3.8 – 4.5.
4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS
4.1 Therapeutic indications
Terrosa is indicated in adults.
Treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women and in men at increased risk of fracture (see section 5.1). In postmenopausal women, a significant reduction in the incidence of vertebral and non-vertebral fractures but not hip fractures has been demonstrated.
Treatment of osteoporosis associated with sustained systemic glucocorticoid therapy in women and men at increased risk for fracture (see section 5.1).
4.2 Posology and method of administration
Posology
The recommended dose of Terrosa is 20 micrograms administered once daily.
Posology Patients should receive supplemental calcium and vitamin D supplements if dietary intake is inadequate.
The maximum total duration of treatment with teriparatide should be 24 months (see section 4.4). The 24-month course of teriparatide should not be repeated over a patient’s lifetime.
Following cessation of teriparatide therapy, patients may be continued on other osteoporosis therapies.
Special populations
Renal impairment
Teriparatide must not be used in patients with severe renal impairment (see section 4.3). In patients with moderate renal impairment, teriparatide should be used with caution. No special caution is required for patients with mild renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment
No data are available in patients with impaired hepatic function (see section 5.3). Therefore, teriparatide should be used with caution.
Paediatric population and young adults with open epiphyses
The safety and efficacy of teriparatide in children and adolescents less than 18 years have not been established. Teriparatide should not be used in paediatric patients (less than 18 years), or young adults with open epiphyses.
Elderly
Dosage adjustment based on age is not required (see section 5.2). Terrosa should be administered once daily by subcutaneous injection in the thigh or abdomen.
Method of administration
Terrosa should be administered once daily by subcutaneous injection in the thigh or abdomen.
It should be administered exclusively with the Terrosa Pen reusable, multidose medicine delivery system and the injection needles which are listed as compatible in the instructions which are provided with the pen. The pen and injection needles are not included with Terrosa. However, for the treatment initiation a cartridge and pen pack should be used containing one carton of Terrosa cartridge and one carton of Terrosa Pen. Terrosa must not be used with any other pen. Patients must be trained to use the proper injection techniques (see section 6.6). An instruction for use which is included in the carton of the delivery system is also available to instruct patients on the correct use of the pen.
The date of first injection should also be written on the outer carton of Terrosa (see the provided space on the box: {First use:}).
4.3 Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1.
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding (see sections 4.4 and 4.6).
- Pre-existing hypercalcaemia.
- Severe renal impairment.
- Metabolic bone diseases (including hyperparathyroidism and Paget’s disease of the bone) other than primary osteoporosis or glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis.
- Unexplained elevations of alkaline phosphatase.
- Prior external beam or implant radiation therapy to the skeleton.
- Patients with skeletal malignancies or bone metastases should be excluded from treatment with teriparatide.
4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use
Serum and urine calcium
In normocalcaemic patients, slight and transient elevations of serum calcium concentrations have been observed following teriparatide injection. Serum calcium concentrations reach a maximum between 4 and 6 hours and return to baseline by 16 to 24 hours after each dose of teriparatide. Therefore, if blood samples for serum calcium measurements are taken, this should be done at least 16 hours after the most recent teriparatide injection. Routine calcium monitoring during therapy is not required.
Teriparatide may cause small increases in urinary calcium excretion, but
the incidence of hypercalciuria did not differ from that in the placebo-treated
patients in clinical trials.
Urolithiasis
Teriparatide has not been studied in patients with active urolithiasis. Teriparatide should be used with caution in patients with active or recent urolithiasis because of the potential to exacerbate this condition.
Orthostatic hypotension
In short-term clinical studies with teriparatide, isolated episodes of transient orthostatic hypotension were observed. Typically, an event began within 4 hours of dosing and spontaneously resolved within a few minutes to a few hours. When transient orthostatic hypotension occurred, it happened within the first several doses, was relieved by placing subjects in a reclining position, and did not preclude continued treatment.
Renal impairment
Caution should be exercised in patients with moderate renal impairment.
Younger adult population
Experience in the younger adult population, including premenopausal women, is limited (see section 5.1). Treatment should only be initiated if the benefit clearly outweighs risks in this population.
Women of childbearing potential should use effective methods of contraception during use of teriparatide. If pregnancy occurs, teriparatide should be discontinued.
Duration of treatment
Studies in rats indicate an increased incidence of osteosarcoma with long-term administration of teriparatide (see section 5.3). Until further clinical data become available, the recommended treatment time of 24 months should not be exceeded.
Documentation
Batch (Lot) number of each cartridge and the date of its first injection should be recorded by the patient on a calendar.
Excipient
This medicinal product contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dosage unit, that is to say essentially “sodium-free”.
4.5 Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
In a study of 15 healthy subjects administered digoxin daily to steady state, a single teriparatide dose did not alter the cardiac effect of digoxin. However, sporadic case reports have suggested that hypercalcaemia may predispose patients to digitalis toxicity. Because teriparatide transiently increases serum calcium, teriparatide should be used with caution in patients taking digitalis.
Teriparatide has been evaluated in pharmacodynamic interaction studies with hydrochlorothiazide. No clinically significant interactions were noted.
Co-administration of raloxifene or hormone replacement therapy with teriparatide did not alter the effects of teriparatide on serum or urine calcium or on clinical adverse events.
4.6 Fertility, pregnancy and lactation
Women of childbearing potential / Contraception in females
Women of childbearing potential should use effective methods of contraception during use of teriparatide. If pregnancy occurs, Terrosa should be discontinued.
Pregnancy
Terrosa is contraindicated for
use during pregnancy (see section 4.3).
Breast-feeding
Terrosa is contraindicated for use during breast-feeding. It is not known whether teriparatide is excreted in human milk.
Fertility
Studies in rabbits have shown reproductive toxicity (see section 5.3). The effect of teriparatide on human foetal development has not been studied. The potential risk for humans is unknown.
4.7 Effects on ability to drive and use machines
Teriparatide has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Transient, orthostatic hypotension or dizziness was observed in some patients. These patients should refrain from driving or the use of machines until symptoms have subsided.
4.8 Undesirable effects
Summary of the safety profile
The most commonly reported adverse reactions in patients treated with teriparatide are nausea, pain in limb, headache and dizziness.
Tabulated list of adverse reactions
Of patients in the teriparatide trials, 82.8% of the teriparatide patients and 84.5% of the placebo patients reported at least 1 adverse event.
The adverse reactions associated with the use of teriparatide in osteoporosis clinical trials and post-marketing exposure are summarised in the table below.
The following convention has been used for the classification of the adverse reactions: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100 to <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1,000 to <1/100), and rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1,000).
| Organ System Class | Very common | Common | Uncommon | Rare |
| Blood and lymphatic system disorders | Anaemia | |||
| Immune system disorders | Anaphylaxis | |||
| Metabolism and nutrition disorders | Hypercholesterolaemia | Hypercalcaemia greater than 2.76 mmol/L, hyperuricaemia | Hypercalcaemia greater than 3.25 mmol/L | |
| Psychiatric disorders | Depression | |||
| Nervous system disorders | Dizziness, headache, sciatica, syncope | |||
| Ear and labyrinth disorders | Vertigo | |||
| Cardiac disorders | Palpitations | Tachycardia | ||
| Vascular disorders | Hypotension | |||
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | Dyspnoea | Emphysema | ||
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Nausea, vomiting, hiatus hernia, gastro-oesophageal reflux disease | Haemorrhoids | ||
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Sweatingincreased | |||
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Pain in limb | Muscle cramps | Myalgia, arthralgia, back cramp/pain* | |
| Renal and urinary disorders | Urinaryincontinence,polyuria,micturitionurgency,nephrolithiasis | Renalfailure/impairment | ||
| General disorders and administration site condition | Fatigue, chest pain, asthenia, mild and transient injection site events, including pain, swelling, erythema, localised bruising, pruritus and minor bleeding at injection site | Injection site erythema, injection site reaction | Possible allergic events soon after injection: acute dyspnoea, oro/facial oedema, generalised urticaria, chest pain, oedema (mainly peripheral) | |
| Investigations | Weight increased, cardiac murmur, alkaline phosphatase increased |
*Serious cases of back cramp or pain have been reported within minutes of the injection. Description of selected adverse reactions
In clinical trials the following reactions were reported at a ≥1% difference in frequency from placebo: vertigo, nausea, pain in limb, dizziness, depression, dyspnoea.
Teriparatide increases serum uric acid concentrations. In clinical trials, 2.8% of teriparatide patients had serum uric acid concentrations above the upper limit of normal compared with 0.7% of placebo patients. However, the hyperuricaemia did not result in an increase in gout, arthralgia, or urolithiasis.
In a large clinical trial, antibodies that cross-reacted with teriparatide were detected in 2.8% of women receiving teriparatide. Generally, antibodies were first detected following 12 months of treatment and diminished after withdrawal of therapy. There was no evidence of hypersensitivity reactions, allergic reactions, effects on serum calcium, or effects on Bone Mineral Density (BMD) response.
Reporting of suspected adverse reactions
Reporting suspected adverse reactions after authorisation of the medicinal product is important. It allows continued monitoring of the benefit/risk balance of the medicinal product. Healthcare professionals are asked to report any suspected adverse reactions via the national reporting system listed in Appendix V.
4.9 Overdose
Signs and symptoms
Teriparatide has been administered in single doses of up to 100 micrograms and in repeated doses of up to 60 micrograms/day for 6 weeks.
The effects of overdose that might be expected include delayed hypercalcaemia and risk of orthostatic hypotension. Nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and headache can also occur.
Overdose experience based on post-marketing spontaneous reports
In post-marketing spontaneous reports, there have been cases of medication error where the entire contents (up to 800 micrograms) of a teriparatide pen have been administered as a single dose. Transient events reported have included nausea, weakness/lethargy and hypotension. In some cases, no adverse events occurred as a result of the overdose. No fatalities associated with overdose have been reported.
Overdose management
There is no specific antidote for teriparatide. Treatment of suspected overdose should include transitory discontinuation of teriparatide, monitoring of serum calcium, and implementation of appropriate supportive measures, such as hydration.
5. PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1 Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Calcium homeostasis, parathyroid hormones and analogues, ATC code:
H05AA02
Terrosa is a biosimilar medicinal product. Detailed information is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency http://www.ema.europa.eu.
Mechanism of action
Endogenous 84-amino -acid parathyroid hormone (PTH) is the primary regulator of calcium and phosphate metabolism in bone and kidney. Teriparatide (rhPTH(1-34)) is the active fragment (1-34) of endogenous human parathyroid hormone. Physiological actions of PTH include stimulation of bone formation by direct effects on bone forming cells (osteoblasts) indirectly increasing the intestinal absorption of calcium and increasing the tubular re-absorption of calcium and excretion of phosphate by the kidney.
Pharmacodynamic effects
Teriparatide is a bone formation agent to treat osteoporosis. The skeletal effects of teriparatide depend upon the pattern of systemic exposure. Once-daily administration of teriparatide increases apposition of new bone on trabecular and cortical bone surfaces by preferential stimulation of osteoblastic activity over osteoclastic activity.
Clinical efficacy
Risk factors
Independent risk factors, for example, low BMD, age, the existence of previous fracture, family history of hip fractures, high bone turnover and low body mass index should be considered in order to identify women and men at increased risk of osteoporotic fractures who could benefit from treatment.
Premenopausal women with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis should be considered at high risk for fracture if they have a prevalent fracture or a combination of risk factors that place them at high risk for fracture (e.g., low bone density, sustained high dose glucocorticoid therapy [e.g., ≥7.5 mg/day for at least 6 months], high underlying disease activity, low sex steroid levels).
[e.g., T-score ≤−2]
Postmenopausal osteoporosis
The pivotal study included 1,637 postmenopausal women (mean age 69.5 years). At baseline, ninety percent of the patients had one or more vertebral fractures, and on average, vertebral BMD was
0.82 g/cm2 (equivalent to a T-score = – 2.6). All patients were offered 1000 mg calcium per day and at least 400 IU vitamin D per day. Results from up to 24 months (median: 19 months) treatment with teriparatide demonstrate statistically significant fracture reduction (Table 1). To prevent one or more new vertebral fractures, 11 women had to be treated for a median of 19 months.
Table 1
Fracture incidence in postmenopausal women
| Placebo | Teriparatide | Relative risk (95% CI) | |
| (N = 544) (%) | (N = 541) (%) | vs. placebo | |
| New vertebral fracture (≥1) a | 14.3 | 5.0 b | 0.35 (0.22, 0.55) |
| Multiple vertebral fractures (≥2) a | 4.9 | 1.1 b | 0.23 (0.09, 0.60) |
| Non-vertebral fragility fractures c | 5.5% | 2.6% d | 0.47 (0.25, 0.87) |
| Major non-vertebral fragility fracturesc (hip, radius, humerus, ribs and pelvis) | 3.9% | 1.5% d | 0.38 (0.17, 0.86) |
Abbreviations: N = number of patients randomly assigned to each treatment group; CI = confidence interval.
a The incidence of vertebral fractures was assessed in 448 placebo and 444 teriparatide patients who had baseline and follow-up spine radiographs.
b p≤0.001 compared with placebo.
c A significant reduction in the incidence of hip fractures has not been demonstrated.
dp≤0.025 compared with placebo.
After 19 months (median) treatment, bone mineral density (BMD) had increased in the lumbar spine and total hip, respectively, by 9% and 4% compared with placebo (p<0.001).
Post-treatment management: Following treatment with teriparatide, 1,262 postmenopausal women from the pivotal trial enrolled in a post-treatment follow-up study. The primary objective of the study was to collect safety data of teriparatide. During this observational period, other osteoporosis treatments were allowed and additional assessment of vertebral fractures was performed.
During a median of 18 months following discontinuation of teriparatide, there was a 41% reduction (p=0.004) compared with placebo in the number of patients with a minimum of one new vertebral fracture.
In an open-label study, 503 postmenopausal women with severe osteoporosis and a fragility fracture within the previous 3 years (83% had received previous osteoporosis therapy) were treated with teriparatide for up to 24 months. At 24 months, the mean increase from baseline in lumbar spine, total hip and femoral neck BMD was 10.5%, 2.6 % and 3.9% respectively. The mean increase in BMD from 18 to 24 months was 1.4%, 1.2%, and 1.6% at the lumbar spine, total hip and femoral neck, respectively.
A 24-month, randomized, double-blind, comparator-controlled Phase 4 study included 1,360 postmenopausal women with established osteoporosis. 680 subjects were randomised to teriparatide
and 680 subjects were randomised to oral risedronate 35 mg/week. At baseline, the women had a mean age of 72.1 years and a median of 2 prevalent vertebral fractures; 57.9% of patients had received previous bisphosphonate therapy and 18.8% took concomitant glucocorticoids during the study. 1,013 (74.5%) patients completed the 24-month follow-up. The mean (median) cumulative dose of glucocorticoid was 474.3 (66.2) mg in the teriparatide arm and 898.0 (100.0) mg in the risedronate arm. The mean (median) vitamin D intake for the teriparatide arm was 1433 IU/day (1400 IU/day) and for the risedronate arm was 1191 IU/day (900 IU/day). For those subjects who had baseline and follow-up spine radiographs, the incidence of new vertebral fractures was 28/516 (5.4%) in teriparatide- and 64/533 (12.0%) in risedronate-treated patients, relative risk (95% CI) = 0.44 (0.29-0.68), p<0.0001. The cumulative incidence of pooled clinical fractures (clinical vertebral and non vertebral fractures) was 4.8% in teriparatide and 9.8% in risedronate-treated patients, hazard ratio (95% CI) = 0.48 (0.32-0.74), p=0.0009.
Male osteoporosis
437 patients (mean age 58.7 years) were enrolled in a clinical trial for men with hypogonadal (defined as low morning free testosterone or an elevated FSH or LH) or idiopathic osteoporosis. Baseline spinal and femoral neck bone mineral density mean T-scores were -2.2 and -2.1, respectively. At baseline, 35% of patients had a vertebral fracture and 59% had a non-vertebral fracture.
All patients were offered 1000 mg calcium per day and at least 400 IU vitamin D per day. Lumbar spine BMD significantly increased by 3 months. After 12 months, BMD had increased in the lumbar spine and total hip by 5% and 1%, respectively, compared with placebo. However, no significant effect on fracture rates was demonstrated.
Glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis
The efficacy of teriparatide in men and women (N=428) receiving sustained systemic glucocorticoid therapy (equivalent to 5 mg or greater of prednisone for at least 3 months) was demonstrated in the 18-month primary phase of a 36-month, randomised, double-blind, comparator -controlled study (alendronate 10 mg/day) . Twenty-eight percent of patients had one or more radiographic vertebral fractures at baseline. All patients were offered 1000 mg calcium per day and 800 IU vitamin D per day.
This study included postmenopausal women (N=277), premenopausal women (N=67), and men (N=83). At baseline, the postmenopausal women had a mean age of 61 years, mean lumbar spine BMD T score of −2.7, median prednisone equivalent dose of 7.5 mg/day, and 34% had one or more radiographic vertebral fractures; premenopausal women had a mean age of 37 years, mean lumbar spine BMD T score of −2.5, median prednisone equivalent dose of 10 mg/day, and 9% had one or more radiographic vertebral fractures; and men had a mean age of 57 years, mean lumbar spine BMD T score of −2.2, median prednisone equivalent dose of 10 mg/day, and 24% had one or more radiographic vertebral fractures.
Sixty-nine percent of patients completed the 18-month primary phase. At the 18 month endpoint, teriparatide significantly increased lumbar spine BMD (7.2%) compared with alendronate (3.4%) (p<0.001) . Teriparatide increased BMD at the total hip (3.6%) compared with alendronate (2.2%) (p<0.01), as well as at the femoral neck (3.7%) compared with alendronate (2.1%) (p<0.05). In patients treated with teriparatide, lumbar spine, total hip and femoral neck BMD increased between 18 and 24 months by an additional 1.7%, 0.9%, and 0.4%, respectively.
At 36 months, analysis of spinal X-rays from 169 alendronate patients and 173 teriparatide patients showed that 13 patients in the alendronate group (7.7%) had experienced a new vertebral fracture compared with 3 patients in the teriparatide group (1.7%) (p=0.01). In addition, 15 of 214 patients in the alendronate group (7.0%) had experienced a non-vertebral fracture compared with 16 of 214 patients in the teriparatide group (7.5%) (p=0.84).
In premenopausal women, the increase in BMD from baseline to 18 month endpoint was significantly greater in the teriparatide group compared with the alendronate group at the lumbar spine (4.2% versus −1.9%; p<0.001) and total hip (3.8% versus 0.9%; p=0.005). However, no significant effect on fracture rates was demonstrated.
5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties
Distribution
The volume of distribution is approximately 1.7 L/kg. The half-life of teriparatide is approximately 1 hour when administered subcutaneously, which reflects the time required for absorption from the injection site.
Biotransformation
No metabolism or excretion studies have been performed with teriparatide but the peripheral metabolism of parathyroid hormone is believed to occur predominantly in liver and kidney.
Elimination
Teriparatide is eliminated through hepatic and extra-hepatic clearance (approximately 62 L/hr in women and 94 L/hr in men).
Elderly
No differences in teriparatide pharmacokinetics were detected with regard to age (range 31 to 85 years). Dosage adjustment based on age is not required.
5.3 Preclinical safety data
Teriparatide was not genotoxic in a standard battery of tests. It produced no teratogenic effects in rats, mice or rabbits. There were no important effects observed in pregnant rats or mice administered teriparatide at daily doses of 30 to 1000 micrograms/kg. However, foetal resorption and reduced litter size occurred in pregnant rabbits administered daily doses of 3 to 100 micrograms/kg. The embryotoxicity observed in rabbits may be related to their much greater sensitivity to the effects of PTH on blood ionised calcium compared with rodents.
Rats treated with near-life time daily injections had dose-dependent exaggerated bone formation and increased incidence of osteosarcoma most probably due to an epigenetic mechanism. Teriparatide did not increase the incidence of any other type of neoplasia in rats. Due to the differences in bone physiology in rats and humans, the clinical relevance of these findings is probably minor. No bone tumours were observed in ovariectomised monkeys treated for 18 months or during a 3-year follow -up period after treatment cessation. In addition, no osteosarcomas have been observed in clinical trials or during the post treatment follow-up study.
Animal studies have shown that severely reduced hepatic blood flow decreases exposure of PTH to the principal cleavage system (Kupffer cells) and consequently clearance of PTH(1-84).
6. PHARMACEUTICAL PARTICULARS
6.1 List of excipients
Glacial acetic acid
Mannitol
Metacresol
Sodium acetate trihydrate
Hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment)
Sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment)
Water for injections
6.2 Incompatibilities
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products.
6.3 Shelf life
2 years.
Chemical in-use stability has been demonstrated for 28 days at 2 – 8 °C.
From a microbiological point of view, once opened, the product may be stored for a maximum of 28 days within its shelf life at 2 °C to 8 °C.
Other in-use storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user.
6.4 Special precautions for storage
Store in a refrigerator (2 °C – 8 °C). After insertion of the cartridge into the pen, the combined pen and cartridge should be returned to the refrigerator immediately after use.
Do not freeze. Keep the cartridge in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
Do not store the injection device with the needle attached. Do not remove the cartridge from the pen after first use.
For storage conditions after first opening of the medicinal product, see section 6.3.
6.5 Nature and contents of container
3 mL cartridge (siliconised Type I glass), with a plunger stopper (bromobutyl) and disc seal (aluminium and rubber liner seals), packed in a plastic tray sealed with lid foil and packed in a carton.
Each cartridge contains 2.4 mL of solution corresponding to 28 doses of 20 micrograms (permicroliters). Pack sizes:
Terrosa 20 micrograms/80 microliters solution for injection:
- or 3 cartridges.
Terrosa cartridge and pen pack:
1 carton of Terrosa cartridge (containing 1 cartridge) and 1 carton of Terrosa Pen (containing 1 pen).
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
6.6 Special precautions for disposal and other handling
Terrosa is supplied in a cartridge. Terrosa cartridges are to be used in Terrosa Pen reusable, multidose pen device exclusively and must not be used with any other pen. No needles are supplied with this medicinal product.
Each cartridge and pen should be used by only one patient. The pen can be used with compatible pen needles. These are listed in the instruction for use for the pen. A new, sterile pen needle must be used for every injection.
The expiry date on the cartridge label must always be checked before inserting the cartridge into Terrosa Pen. To avoid medication errors make sure that the date when starting to use a new cartridge is at least 28 days before its expiry date.
Before using the pen device for the first time, the patient should read and understand the instructions on how to use the pen which are provided with the pen.
After each injection, the pen should be returned to the refrigerator. After the first use, the cartridge should not be removed from the pen during the 28 days of usage.
Terrosa must not be transferred to a syringe.
Empty cartridges must not be refilled.
Terrosa should not be used if the solution is cloudy, coloured or contains visible particles.
Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
7. MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Gedeon Richter Plc.
Gyömrői út 19-21.
1103 Budapest
Hungary
8. MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/16/1159/001 [1 cartridge]
EU/1/16/1159/002 [3 cartridges]
EU/1/16/1159/003 [cartridge and pen pack]
9. DATE OF FIRST AUTHORISATION / RENEWAL OF THE AUTHORISATION
Date of first authorisation: 04 January 2017
10. DATE OF REVISION OF THE TEXT
Detailed information on this product is available on the website of the European Medicines Agency http://www.ema.europa.eu
A. Manufacturer of the biological active substance and manufacturer responsible for batch release
Name and address of the manufacturer of the biological active substance
Richter-Helm BioLogics GmbH & Co. KG
Dengelsberg
24796 Bovenau
GERMANY
Name and address of the manufacturer responsible for batch release
Gedeon Richter Plc.
Gyömrői út 19-21
1103 Budapest
HUNGARY
B. Conitions or restrictions regarding supply and use
Medicinal product subject to medical prescription.
C. Other conditions and requirements of the marketing authorisation
- Periodic safety update reports
The requirements for submission of periodic safety update reports for this medicinal product are set out in the list of Union reference dates (EURD list) provided for under Article 107c(7) of Directive 2001/83/EC and any subsequent updates published on the European medicines web-portal.
D. Conditions or restrictions with regard to the safe and effective use of the medicinal product
- Risk Management Plan (RMP)
The MAH shall perform the required pharmacovigilance activities and interventions detailed in the agreed RMP presented in Module 1.8.2 of the marketing authorisation and any agreed subsequent updates of the RMP.
An updated RMP should be submitted:
- At the request of the European Medicines Agency;
- Whenever the risk management system is modified, especially as the result of new information being received that may lead to a significant change to the benefit/risk profile or as the result of an important (pharmacovigilance or risk minimisation) milestone being reached.
Labelling
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING OUTER CARTON FOR CARTRIDGE AND PEN PACK
1.NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Terrosa 20 micrograms/80 microliters solution for injection teriparatide
2.STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each dose of 80 microliters contains 20 micrograms of teriparatide.
Each cartridge contains 28 doses of 20 micrograms (per 80 microliters).
3.LIST OF EXCIPIENTS
Glacial acetic acid, sodium acetate trihydrate, mannitol, metacresol, water for injections, hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment) and sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment).
4.PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solution for injection
1 Terrosa cartridge
1 Terrosa Pen
Not to be sold separately.
5.METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
The cartridge and pen pack should be used for treatment initiation. Do not remove the cartridge from the pen during the 28 days of use.
Read both the package leaflet of Terrosa cartridge and the instructions for use of the Terrosa Pen before use.
Subcutaneous use.

6.SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT OF THE SIGHT AND REACH OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the sight and reach of children.
7.OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
8.EXPIRY DATE
EXP:
9.SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator.
Do not freeze.
10.SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF APPROPRIATE
11.NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Gedeon Richter Plc.
Gyömrői út 19-21.
1103 Budapest Hungary
12.MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/16/1159/003 [cartridge and pen pack]
13.BATCH NUMBER
Lot
14.GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
15.INSTRUCTIONS ON USE
16.INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Terrosa cartridge and pen
17.UNIQUE IDENTIFIER – 2D BARCODE
2D barcode carrying the unique identifier included
18.UNIQUE IDENTIFIER – HUMAN READABLE DATA
PC:
SN:
NN:
PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON THE OUTER PACKAGING OUTER CARTON FOR CARTRIDGE
1.NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Terrosa 20 micrograms/80 microliters solution for injection teriparatide
2.STATEMENT OF ACTIVE SUBSTANCE(S)
Each dose of 80 microliters contains 20 micrograms of teriparatide.
Each cartridge contains 28 doses of 20 micrograms (per 80 microliters).
3.LIST OF EXCIPIENTS
Glacial acetic acid, sodium acetate trihydrate, mannitol, metacresol, water for injections, hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment) and sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment).
4.PHARMACEUTICAL FORM AND CONTENTS
Solution for injection
- cartridge
- cartridges
5.METHOD AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Use only with Terrosa Pen.
Read the package leaflet before use.
Subcutaneous use.

6.SPECIAL WARNING THAT THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MUST BE STORED OUT OF THE SIGHT AND REACH OF CHILDREN
Keep out of the sight and reach of children.
7.OTHER SPECIAL WARNING(S), IF NECESSARY
Do not remove the cartridge from the pen during the 28 days of use.
8.EXPIRY DATE
EXP
Discard the cartridge 28 days after the first use.
First use: 1. ………………………/2 ……………………… /3
9.SPECIAL STORAGE CONDITIONS
Store in a refrigerator.
Do not freeze.
Keep the cartridge in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
10.SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL OF UNUSED MEDICINAL PRODUCTS OR WASTE MATERIALS DERIVED FROM SUCH MEDICINAL PRODUCTS, IF APPROPRIATE
11.NAME AND ADDRESS OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Gedeon Richter Plc.
Gyömrői út 19-21.
1103 Budapest
Hungary
12.MARKETING AUTHORISATION NUMBER(S)
EU/1/16/1159/001 [1 cartridge]
EU/1/16/1159/002 [3 cartridges]
{Displayed in case of 1x and 3x cartridges only. Not applicable in case of cartridge and pen pack.}
13.BATCH NUMBER
Lot
14.GENERAL CLASSIFICATION FOR SUPPLY
15.INSTRUCTIONS ON USE
16.INFORMATION IN BRAILLE
Terrosa cartridge
17.UNIQUE IDENTIFIER – 2D BARCODE
2D barcode carrying the unique identifier included
{Not applicable in case of cartridge and pen pack.}
18.UNIQUE IDENTIFIER – HUMAN READABLE DATA
PC:
SN:
NN:
{Not applicable in case of cartridge and pen pack.}
MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON BLISTERS OR STRIPS LID FOIL
1.NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
Terrosa 20 micrograms/80 microliters solution for injection teriparatide
2.NAME OF THE MARKETING AUTHORISATION HOLDER
Gedeon Richter Plc.
3.EXPIRY DATE
EXP
4.BATCH NUMBER
Lot
5.OTHER
Subcutaneous use {1x}
SC{3x}
Store in a refrigerator.
MINIMUM PARTICULARS TO APPEAR ON SMALL IMMEDIATE PACKAGING UNITS LABEL
1.NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT AND ROUTE(S) OF ADMINISTRATION
Terrosa 20 mcg/80 mcL injection
teriparatide
SC
2.METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION
3.EXPIRY DATE
EXP
3.BATCH NUMBER
Lot
4.CONTENTS BY WEIGHT, BY VOLUME OR BY UNIT
2.4 mL
5.OTHER
Package leaflet
Package leaflet: Information for the user
Terrosa 20 micrograms/80 microliters solution for injection
Teriparatide
This medicine is subject to additional monitoring. This will allow quick identification of new safety information. You can help by reporting any side effects you may get. See the end of section 4 for how to report side effects.
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet. You may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
What is in this leaflet
- What Terrosa is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you use Terrosa
- How to use Terrosa
- Possible side effects
- How to store Terrosa
- Contents of the pack and other information
- Contents of the pack and other information
1.What Terrosa is and what it is used for
Terrosa contains the active substance teriparatide that is used to make the bones stronger, and to reduce the risk of fractures by stimulating bone formation.
Terrosa is used to treat osteoporosis in adults. Osteoporosis is a disease that causes your bones to become thin and fragile. This disease is especially common in women after the menopause, but it can also occur in men. Osteoporosis is also common in patients receiving medicines called corticosteroids.
2.What you need to know before you use Terrosa
Do not use Terrosa:
- if you are allergic to teriparatide or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you have high levels of calcium in your blood (hypercalcaemia).
- if you suffer from serious kidney problems.
- if you have ever had bone cancer or if other cancers have spread (metastasised) to your bones.
- if you have certain bone diseases. If you have a bone disease, tell your doctor.
- if you have unexplained high levels of alkaline phosphatase in your blood, which means you might have Paget’s disease of bone (disease with abnormal bone changes). If you are not sure, ask your doctor.
- if you have had radiation therapy involving your bones.
- if you are pregnant or breast-feeding.
Warning and precautions
Terrosa may increase calcium in your blood or urine.
Talk to your doctor before or while using Terrosa:
- if you have continuing nausea, vomiting, constipation, low energy, or muscle weakness. These
may be signs there is too much calcium in your blood.
- if you suffer from kidney stones or have had kidney stones.
- if you suffer from kidney problems (moderate renal impairment).
Some patients get dizzy or get a fast heartbeat after the first few doses of Terrosa. For the first doses, inject Terrosa in a place where you can sit or lie down right away if you get dizzy.
The recommended treatment time of 24 months should not be exceeded.
Before inserting a cartridge in Terrosa Pen write down the batch (Lot) number of the cartridge and its first injection date on a calendar. The date of first injection should also be recorded on the outer carton of Terrosa (see the provided space on the box: {First use:}) (see section 3.).
Terrosa should not be used in growing adults.
Children and adolescents
Terrosa should not be used in children and adolescents (aged less than 18 years).
Other medicines and Terrosa
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used or might use any other medicines. This is important, because some medicines (e.g. digoxin/digitalis, a medicine used to treat heart disease) may interact with teriparatide.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Do not use Terrosa if you are pregnant or breast-feeding. If you are a woman of child-bearing potential, you should use effective methods of contraception during use of Terrosa. If you become pregnant while using Terrosa, Terrosa should be discontinued. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking any medicine.
Driving and using machines
Some patients may feel dizzy after injecting Terrosa. If you feel dizzy you should not drive or use machines until you feel better.
Terrosa contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol sodium (23 mg) per dosage unit, that is to say essentially “sodium-free”.
3. How to use Terrosa
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
The recommended dose is 20 micrograms (corresponding to 80 microliters) given once a day by injection under the skin (subcutaneous injection) in the thigh or abdomen.
To help you remember to take your medicine, inject it at about the same time each day. Terrosa can be injected at meal times. Inject Terrosa each day for as long as your doctor prescribes it for you. The total duration of treatment with Terrosa should not exceed 24 months. You should not receive more than one treatment course of 24 months over your lifetime.
Your doctor may advise you to take Terrosa with calcium and vitamin D. Your doctor will tell you how much you should take each day.
Terrosa can be given with or without food.
Terrosa cartridges are designed to be used only with the Terrosa Pen reusable, multidose delivery system and compatible pen needles. The pen and injection needles are not included with Terrosa. However, for treatment initiation a cartridge and pen pack should be used containing one carton of
Terrosa cartridge and one carton of Terrosa Pen.
Before the first use, insert the cartridge into the pen. For the correct use of this medicine it is very important to closely follow the detailed Instructions for Use of your pen which are provided with the pen.
Use a new injection needle for each injection to prevent contamination and safely dispose of the needle after use.
Never store your pen with the needle attached.
Never share your pen with others.
Do not use your Terrosa Pen to inject any other medicine (e.g. insulin).
The pen is customised for use with Terrosa only.
Do not refill the cartridge.
Do not transfer the medicine into a syringe.
You should inject Terrosa shortly after you take the pen with inserted cartridge out of the refrigerator. Put the pen with inserted cartridge back into the refrigerator immediately after you have used it. Do not remove the cartridge from the pen after each use. Store it in the cartridge sleeve during the whole 28-day treatment period.
Preparing the pen for use
- To ensure the correct administration of Terrosa always read the Instructions for Use of Terrosa Pen, which is included in the carton of the pen.
- Wash your hands before handling the cartridge or pen.
- Check the expiry date on the cartridge label before inserting the cartridge into the pen. Make sure that there are at least 28 days remaining before its expiry date. Insert the cartridge into the pen before the first use as detailed in the pen instructions. Write down the batch (Lot) number of each cartridge and its first injection date on a calendar. The date of first injection should also be recorded on the outer carton of Terrosa (see the provided space on the box: {First use:}).
- After inserting a new cartridge and before the first injection from this cartridge prime the pen according to the instructions which are provided. Do not prime again after the first dose.
Injecting Terrosa
- Before you inject Terrosa, clean your skin where you intend to inject (thigh or abdomen) as instructed by your doctor.
- Gently hold a fold of cleansed skin and insert the needle straight into the skin. Press the push button and hold it pressed in until the dose indication has returned to the start position.
- After your injection, leave the needle in the skin for six seconds to make sure that you receive the whole dose.
- As soon as you have finished the injection, attach the outer needle protective cap on the pen needle and screw the cap anti-clockwise to remove the pen needle. This will keep the remaining Terrosa sterile and prevent leaking from the pen. It will also stop air going back into the cartridge and the needle from clogging.
- Replace the cap on your pen. Leave the cartridge in the pen.
If you use more Terrosa than you should
If, by mistake, you have used more Terrosa than you should, contact your doctor or pharmacist.
The expected effects of overdose include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and headache.
If you forget to use Terrosa
If you forget an injection or cannot use your medicine at your usual time, inject it as soon as possible on that day. Do not use a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose. Do not take more than one injection in the same day.
If you stop using Terrosa
If you are considering stopping Terrosa treatment, please discuss this with your doctor. Your doctor will advise you and decide how long you should be treated with Terrosa.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The most common side effects are pain in limb (which may affect more than 1 in 10 people). Other common side effects (affecting up to 1 in 10 people) include feeling sick, headache and dizziness. If you become dizzy (light-headed) after your injection, you should sit or lie down until you feel better. If you do not feel better, you should call a doctor before you continue treatment. Cases of fainting have occured after teriparatide use.
If you have discomfort around the area of the injection such as redness of the skin, pain, swelling, itching, bruising or minor bleeding (which can occur in up to 1 in 10 people), this should clear up in a few days or weeks. Otherwise tell your doctor.
Rarely, patients may suffer allergic reactions consisting of breathlessness, swelling of the face, rash and chest pain. These reactions usually occur soon after injection. In rare cases, serious and potentially life-threatening allergic reactions including anaphylaxis can occur.
Other side effects include:
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- increase in blood cholesterol levels
- depression
- nerve pain in the leg
- feeling faint
- spinning sensation
- irregular heartbeats
- breathlessness
- increased sweating
- muscle cramps
- loss of energy
- tiredness
- chest pain
- low blood pressure
- heartburn (painful or burning sensation just below the breast bone)
- vomiting
- a hernia of the tube that carries food to your stomach (hiatus hernia)
- low haemoglobin or red blood cell count (anaemia).
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- increased heart rate
- abnormal heart sound
- shortness of breath
- piles (haemorrhoids)
- leakage of urine
- increased need to pass water
- weight increase
- kidney stones
- pain in the muscles and pain in the joints. Some patients have had severe back cramps or pain which led to admission into hospital.
- increase in blood calcium level
- increase in blood uric acid level
- increase in an enzyme called alkaline phosphatase.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- reduced kidney function, including renal failure
- swelling, mainly in the hands, feet and legs.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly via the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
- How to store Terrosa
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton and the cartridge after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Store in a refrigerator (2 °C – 8 °C). Do not freeze.
Keep the cartridge in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
You can use Terrosa for up to 28 days after the first injection, as long as the cartridge/pen with the cartridge inserted is stored in a refrigerator (2 °C to 8 °C).
Avoid placing the cartridge close to the ice compartment of the refrigerator to prevent freezing. Do not use Terrosa if it is, or has been, frozen.
Each cartridge should be properly disposed of after 28 days of first use, even if it is not completely empty.
Terrosa contains a clear and colourless solution. Do not use Terrosa if solid particles appear or if the solution is cloudy or coloured.
Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use. These measures will help protect the environment.
- Contents of the pack and other information
What Terrosa contains
- The active substance is teriparatide. Each dose of 80 microliters contains 20 micrograms of teriparatide. One cartridge of 2.4 mL contains 600 micrograms of teriparatide (corresponding to 250 micrograms per mL).
- The other ingredients are: glacial acetic acid, mannitol, metacresol, sodium acetate trihydrate, hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment), sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), water for injections.
What Terrosa looks like and contents of the pack
Terrosa is a colourless and clear solution. It is supplied in a cartridge. Each cartridge contains 2.4 mL of solution, enough for 28 doses.
Terrosa 20 micrograms/80 microliters solution for injection: 1 or 3 cartridge(s) packed in a plastic tray sealed with lid foil and packed in a carton.
Terrosa cartridge and pen pack: 1 Terrosa cartridge packed in a plastic tray sealed with lid foil and packed in a carton and 1 Terrosa Pen packed into a separate carton.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Gedeon Richter Plc.
Gyömrői út 19-21.
1103 Budapest
Hungary
This leaflet was last revised in
Other sources of information
Detailed and updated information on this product is available by scanning the QR code included below or the outer carton with a smartphone.The same information is also available on the following URL: www.terrosapatient.com
QR code to be included
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the European Medicines Agency web site:
Instructions for use
Terrosa Pen
Always follow instructions provided below and on the back page when using the Terrosa Pen. Terrosa Pen parts
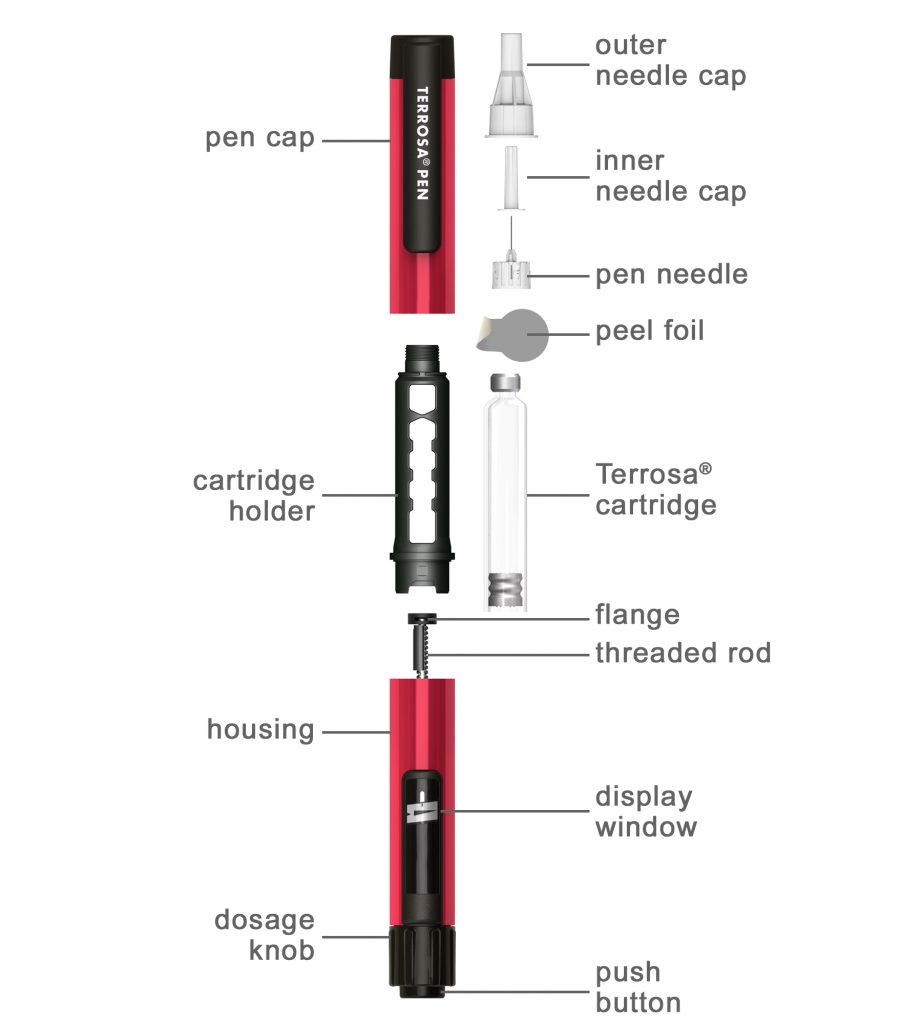
push button; display window; threaded rod; flange; Terrosa cartridge; peel foil; pen needle; inner needle cap; outer needle cap; pen cap; cartridge holder, dosage knob, housing
Pen preparation – First use/changing cartridges
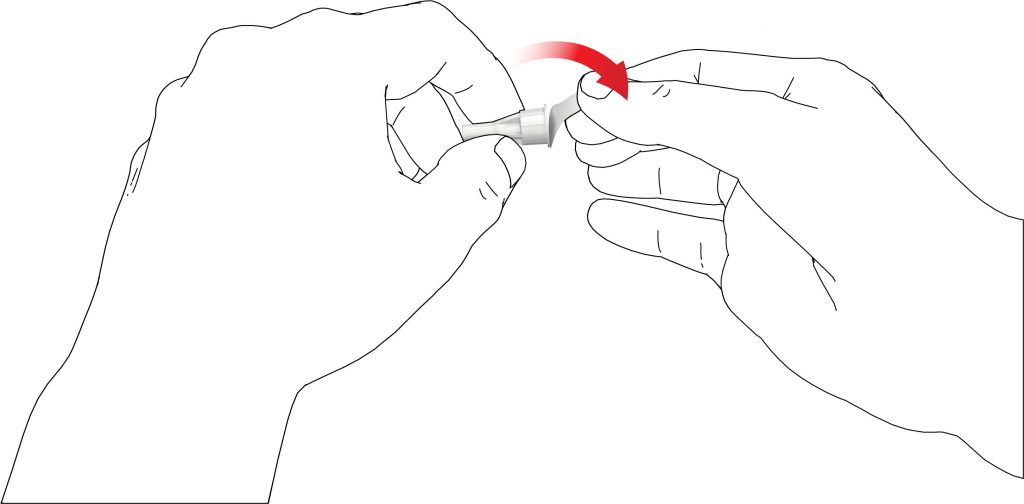
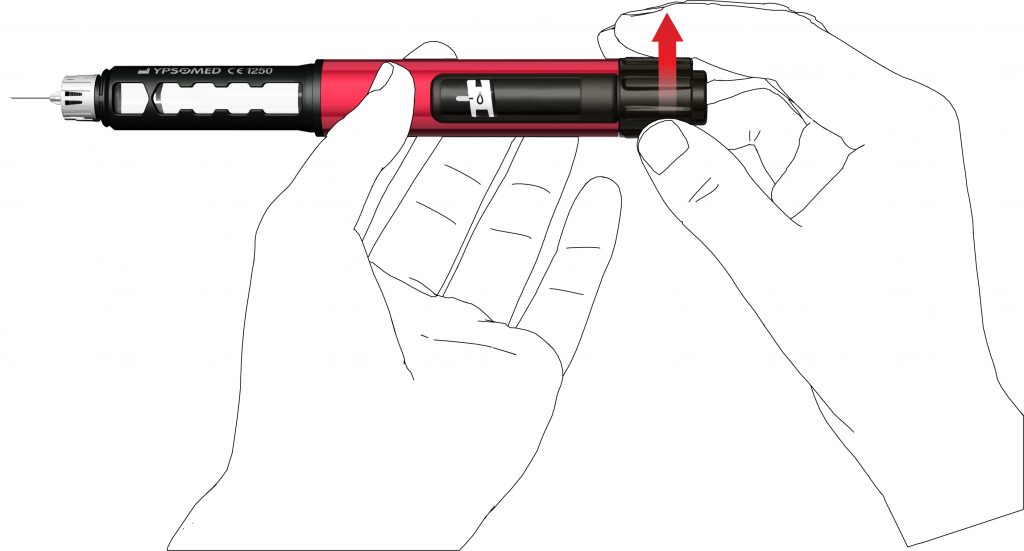
Follow the instructions every time you insert a new Terrosa cartridge into your Terrosa Pen. Do not repeat this before each daily injection, otherwise you will not have enough Terrosa for 28 days. Read the patient information leaflet for Terrosa cartridge provided separately. A: Remove the pen cap.
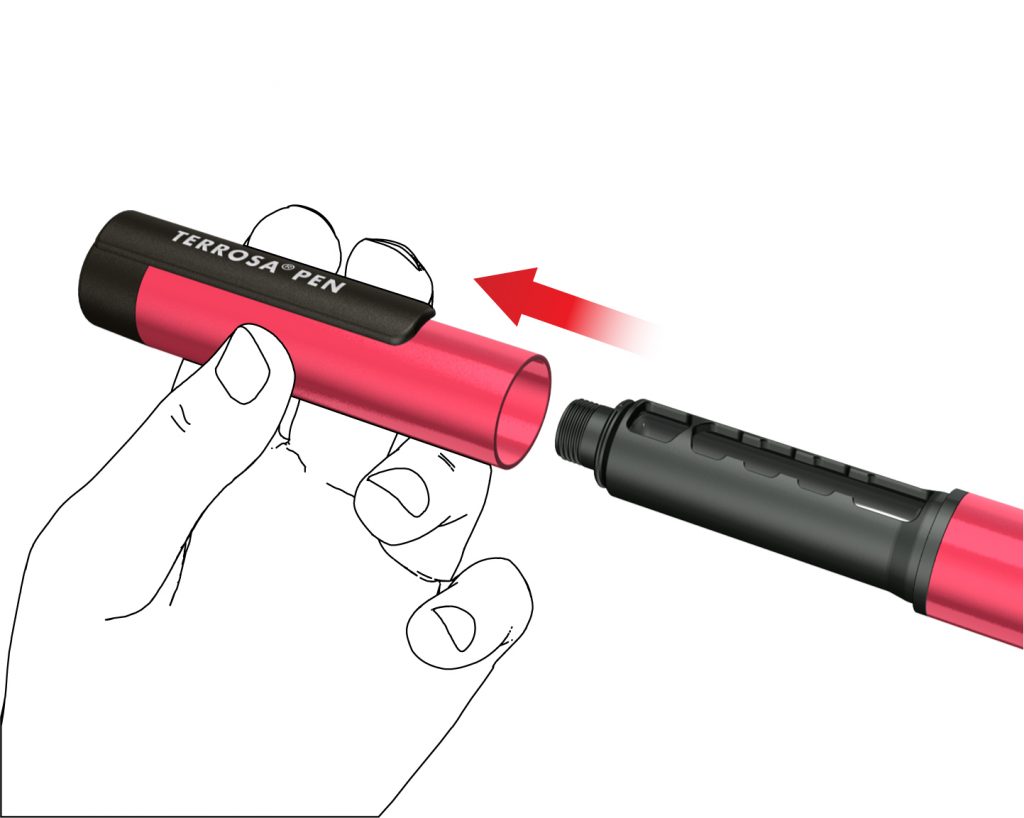
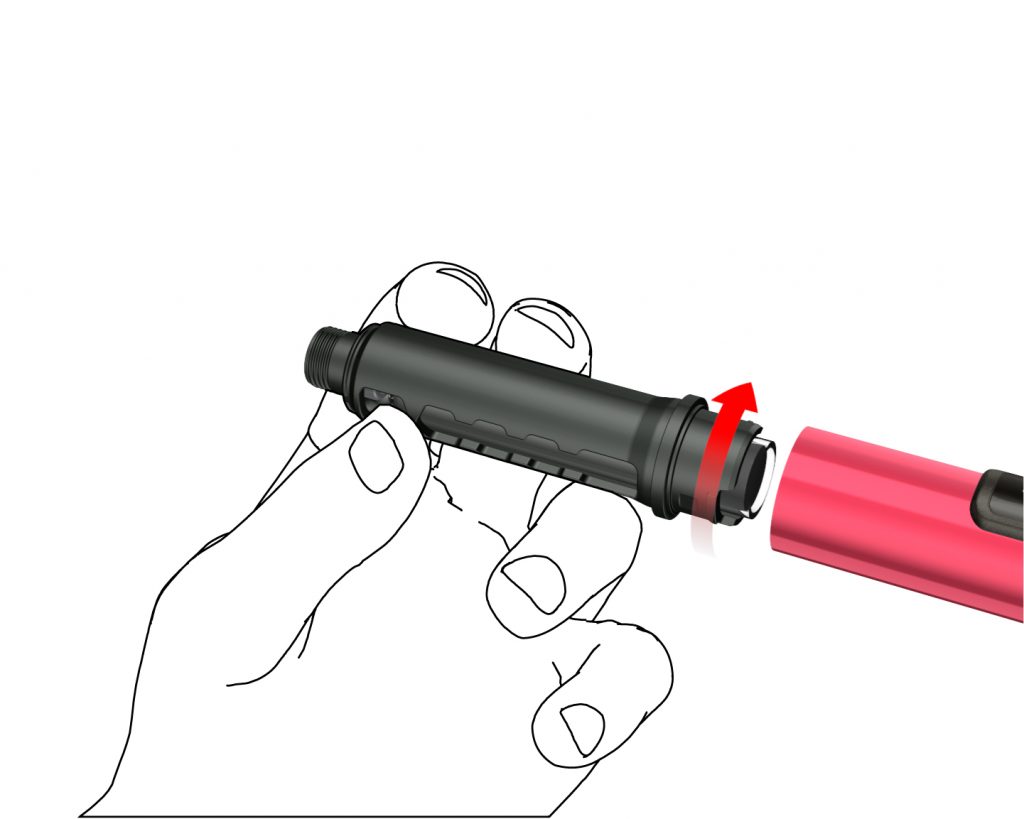
B: Remove the cartridge holder by turning it (bayonet coupling).
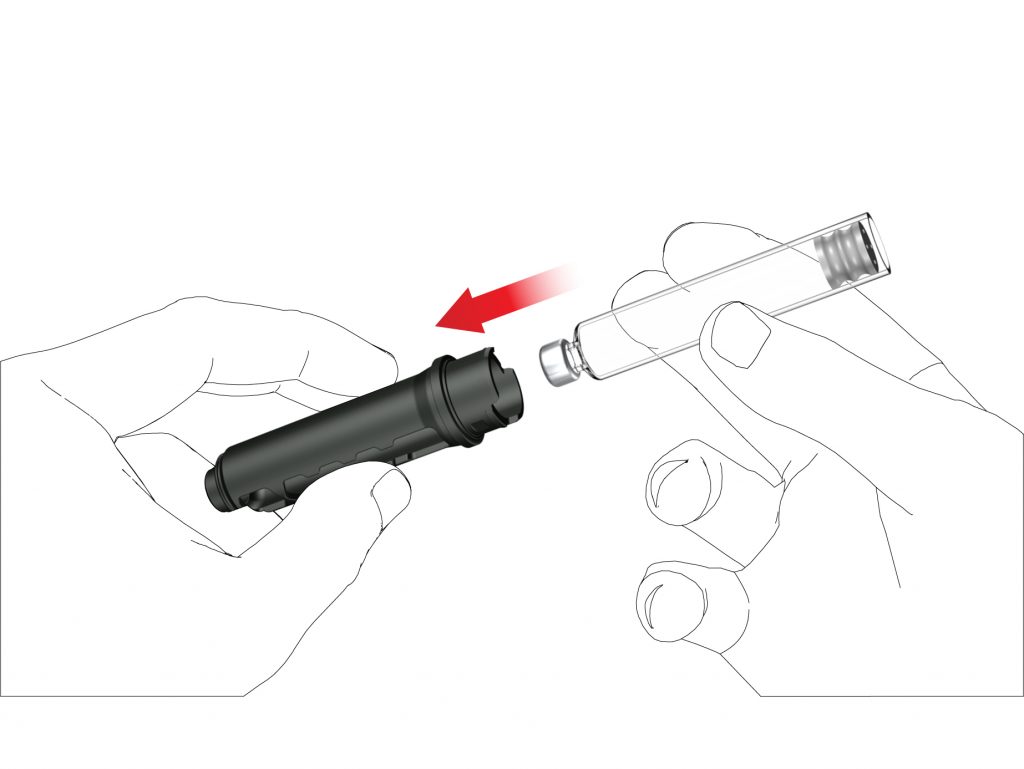
C: Remove the empty cartridge, in the case of changing cartridge. Insert a new Terrosa cartridge into the cartridge holder, with the metal crimped cap of the cartridge first.
Write down the first injection date of each new cartridge. This helps you to know when the 28 daily doses per cartridge are used.
D: Push back the threaded rod carefully with your finger, in a straight line and as far as it will go. This is not necessary when the rod is already in the starting position, such as at the very first use. The threaded rod cannot be pushed back to the pen housing entirely.
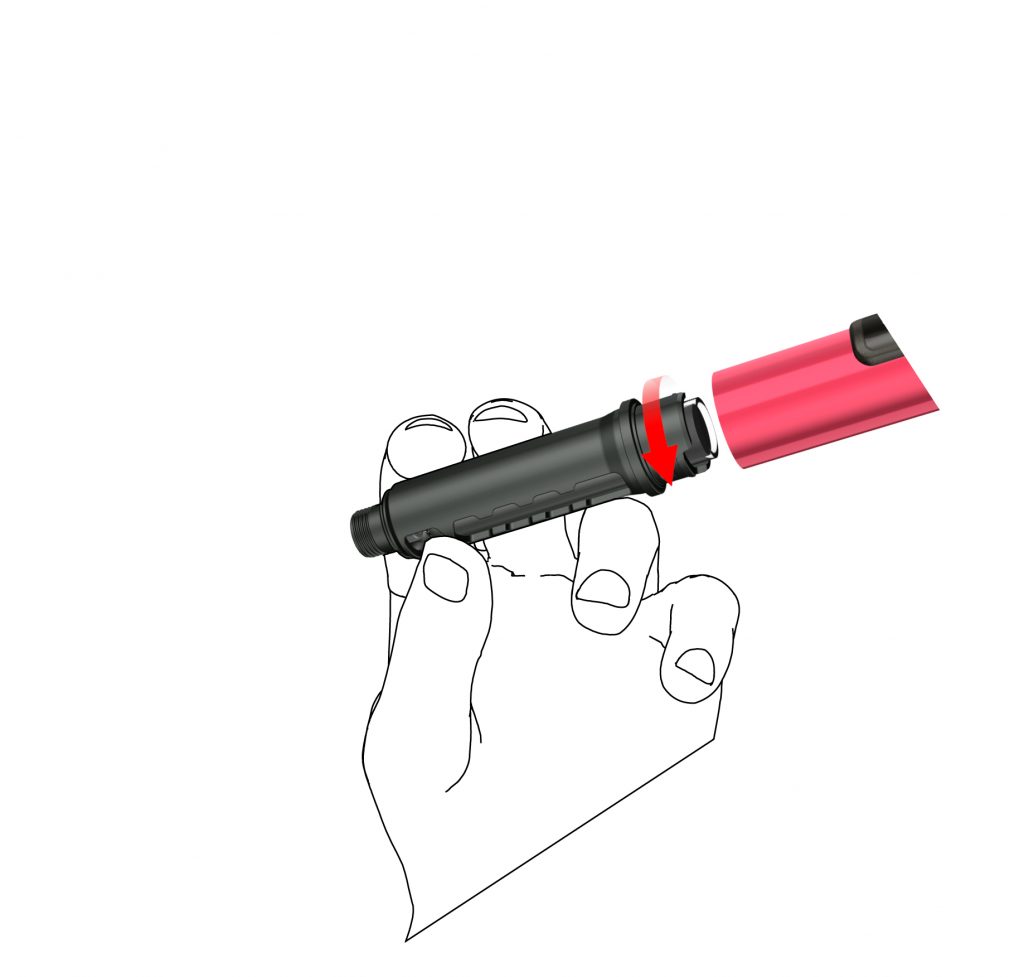
E: Attach the cartridge holder to the housing by turning it 90 degrees, until it stops.
F: Attach a new pen needle as follows:
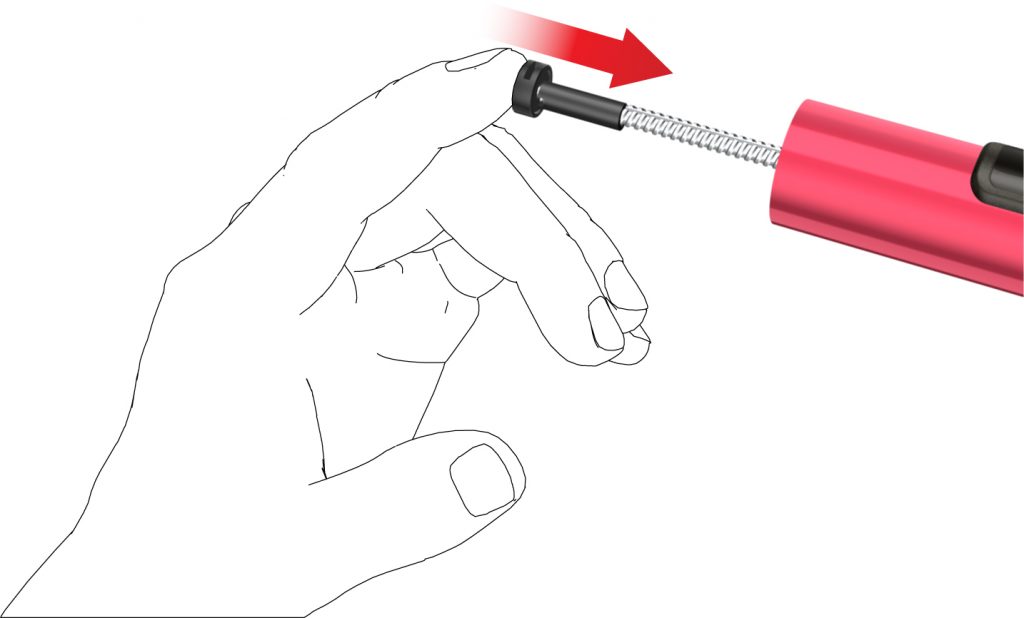
• Pull off the peel foil.
- • Screw the pen needle clockwise onto the cartridge holder. Make sure that the pen needle is attached correctly and sits firmly on the cartridge holder.
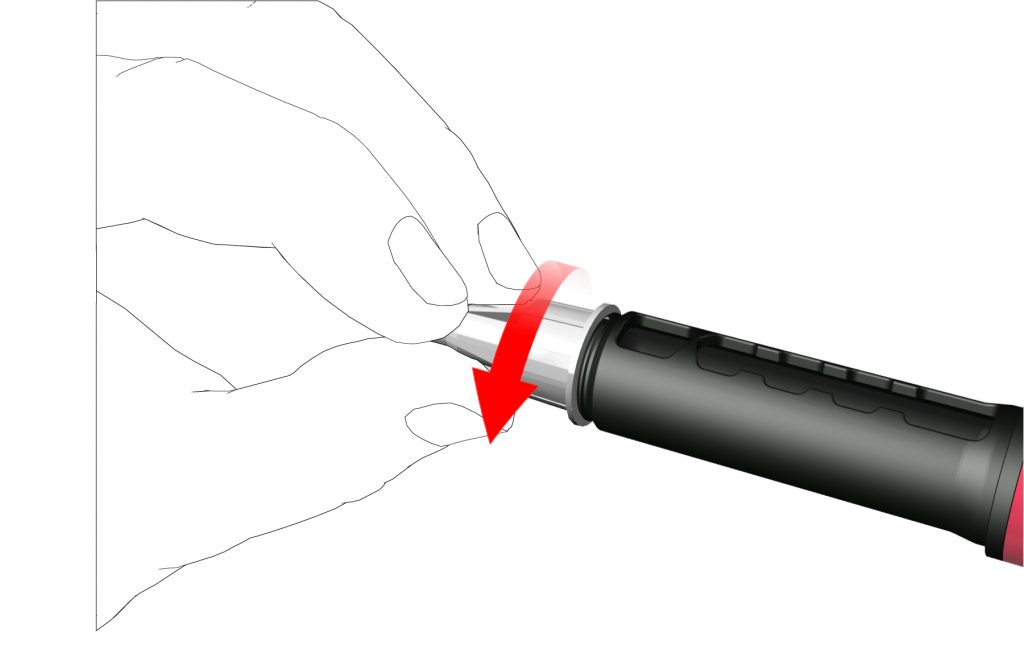
- Remove the outer needle cap and save it.
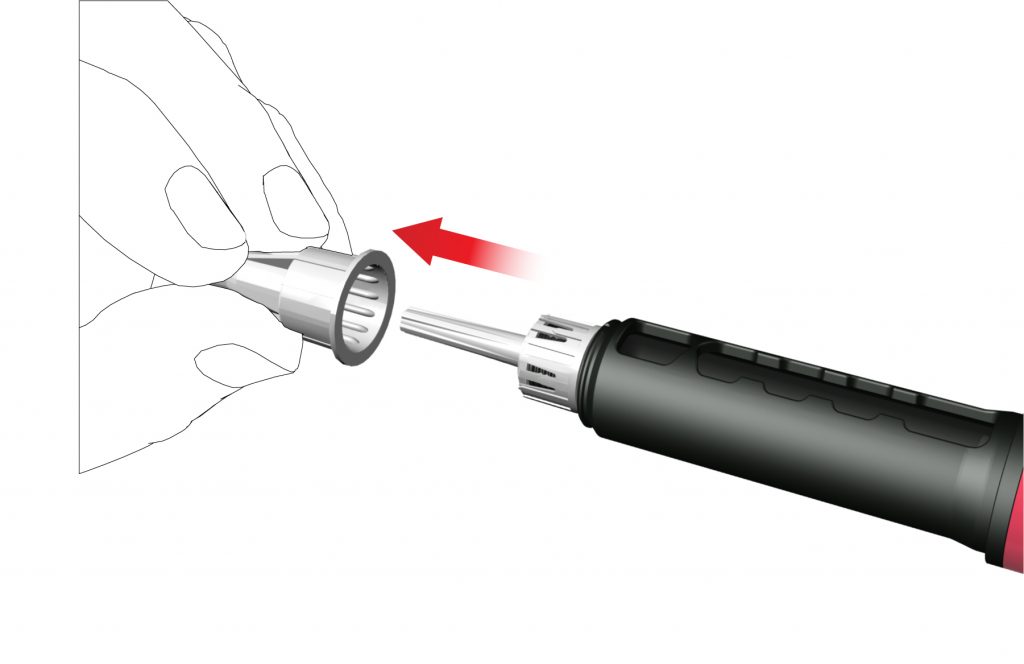
- Remove and dispose the inner needle cap.
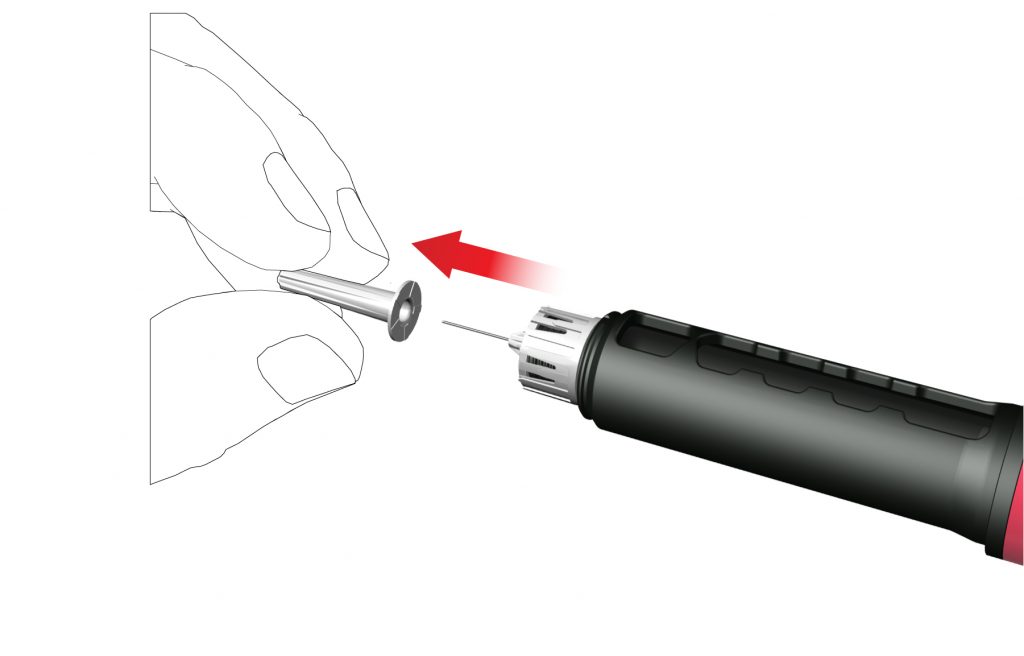
While attaching the needle some drops may escape, this is normal.
G: Priming
The pen must be primed and tested after inserting a new cartridge and prior the first injection from each cartridge.
- Turn the dose knob clockwise until you see a droplet sign on the dose display. Make sure that the two indicator stripes are aligned. During dose dialling the pen provides an audible clicking sound and a noticeable resistance.
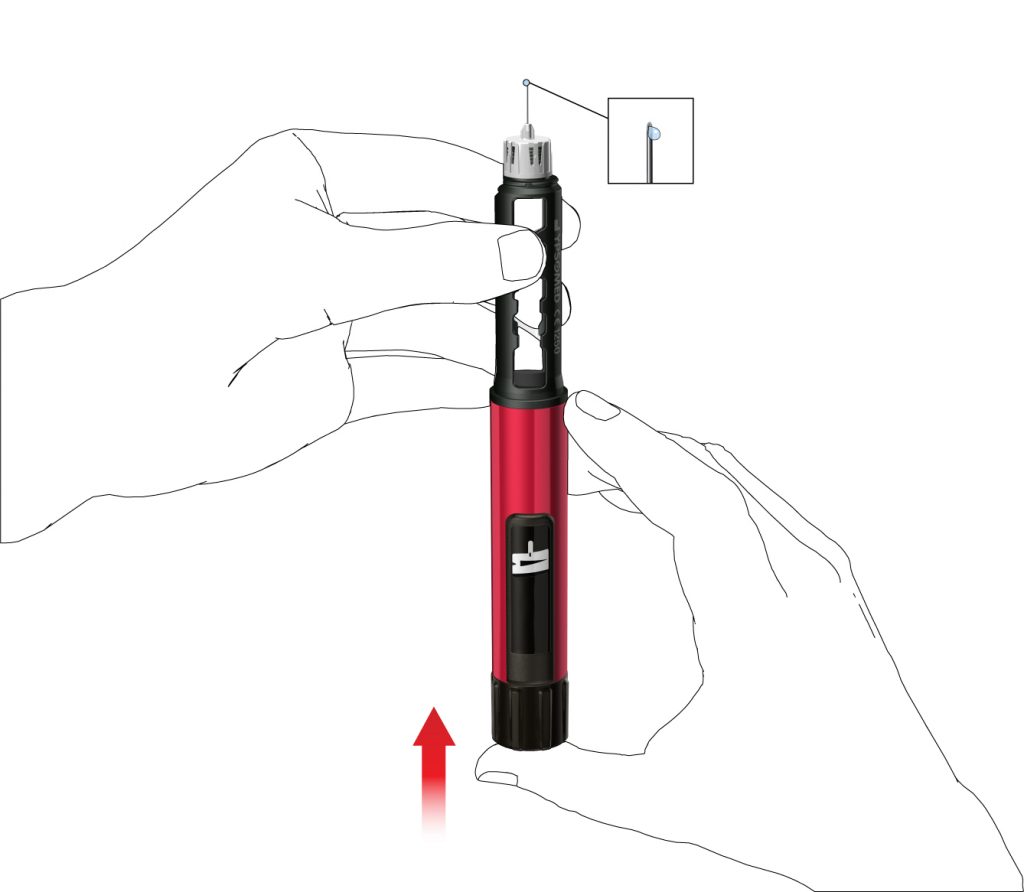
- Hold the pen with the needle pointing upwards.
- Press the push button fully in. Hold it pressed in until the dose indication has turned back to the start position. Some drops of medicine must be expelled from the needle tip.
If no drops emerge, repeat step G until you see some drops. Do not repeat step G more than four times, but follow the instructions given under Troubleshooting section on the back page.
Administration using the Terrosa Pen
Wash your hands carefully with soap to minimise the risk of infection.
Make sure you have ready:
- your Terrosa Pen with inserted cartridge
- a compatible pen needle
- a puncture-resistant sharps disposal container for used needles.
Do not use the pen if the cartridge is cloudy, discoloured or contains particles.
Read the patient information leaflet for Terrosa cartridge provided separately.
1. Attach the pen needle
Use a new needle for every injection. Do not use the pen needle if the packaging is damaged or not opened by yourself.
Note: There is no need to change the needle when using directly after the pen preparation. In this casecontinue with step “2. Setting the dose and injection”.
- Pull off the peel foil.
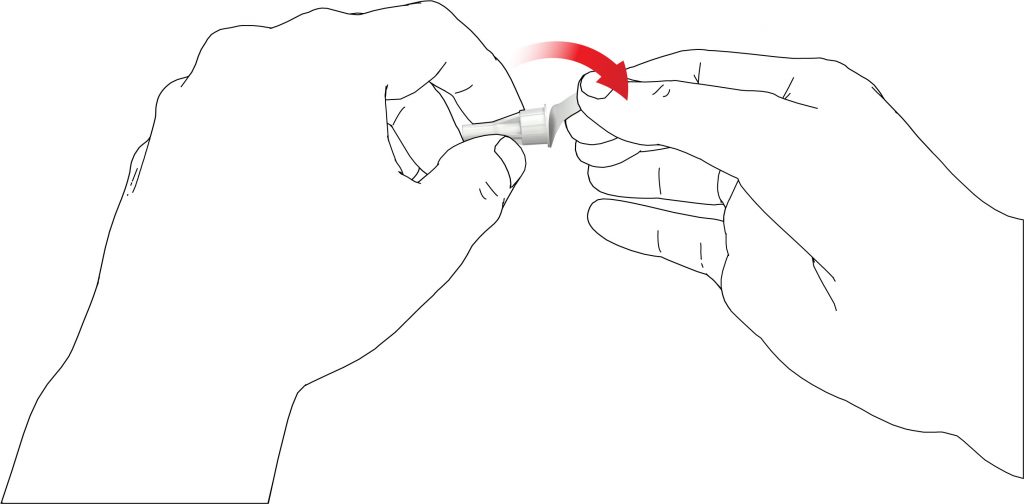
- Screw the pen needle clockwise onto the cartridge holder. Make sure that the pen needle is attached correctly and sits firmly on the cartridge holder.
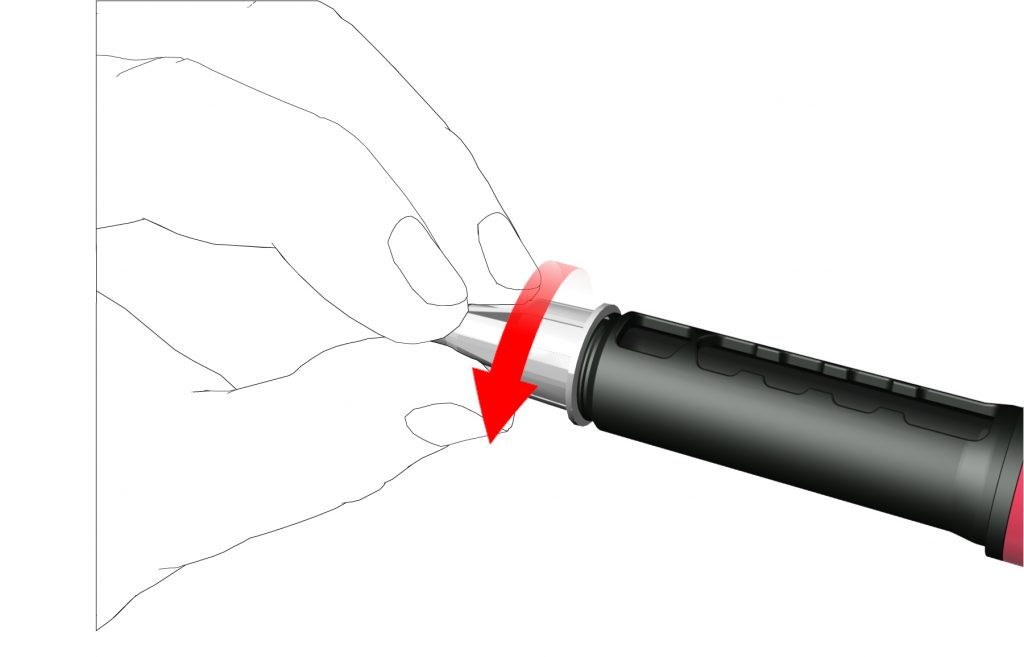
- Remove the outer needle cap and save it.
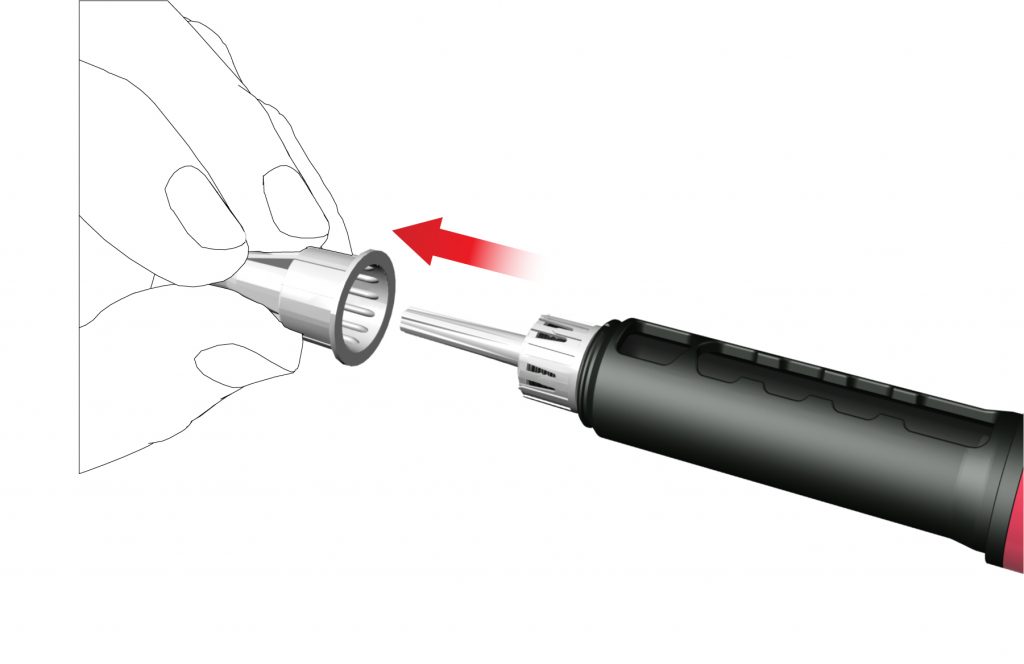
- Remove and dispose the inner needle cap.

While attaching the needle some drops may escape, this is normal.
2. Setting the dose and injection
Warning: Ensure the use of the correct drug liquid. Check the label of the cartridge before itsinsertion into the cartridge holder.
- To set the fixed daily dose of 80 microliters, turn the dose knob clockwise until it stops and cannot be rotated any further. Make sure the display shows an arrow sign and the two indicator stripes are aligned. During dose dialling the pen provides an audible clicking sound and a noticeable resistance. Do not try to force the dose knob any further.

Note: If the cartridge contains less than 80 microliters, the dose knob cannot be turned clockwise up tothe arrow sign. In this case, remove the pen needle, change the cartridge and proceed with priming according the pen preparation steps.
- Select an appropriate injection site and prepare your skin as recommended by your doctor. Gently hold a skin fold between the thumb and index finger. Insert the needle straight and gently into the skin, as shown in the illustration.
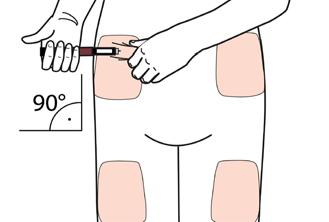
Warning: Prevent the pen needle from bending or breaking. Do not tilt the pen after the needle hasbeen inserted into the skin. Tilting the pen may result in bending or breaking of the needle. Broken needles can get stuck in the skin. Immediately consult the doctor if a broken needle gets stuck in the skin.
- Press the push button until the dose indication has returned to the start position. Keep the needle in the skin fold for a further 6 seconds.
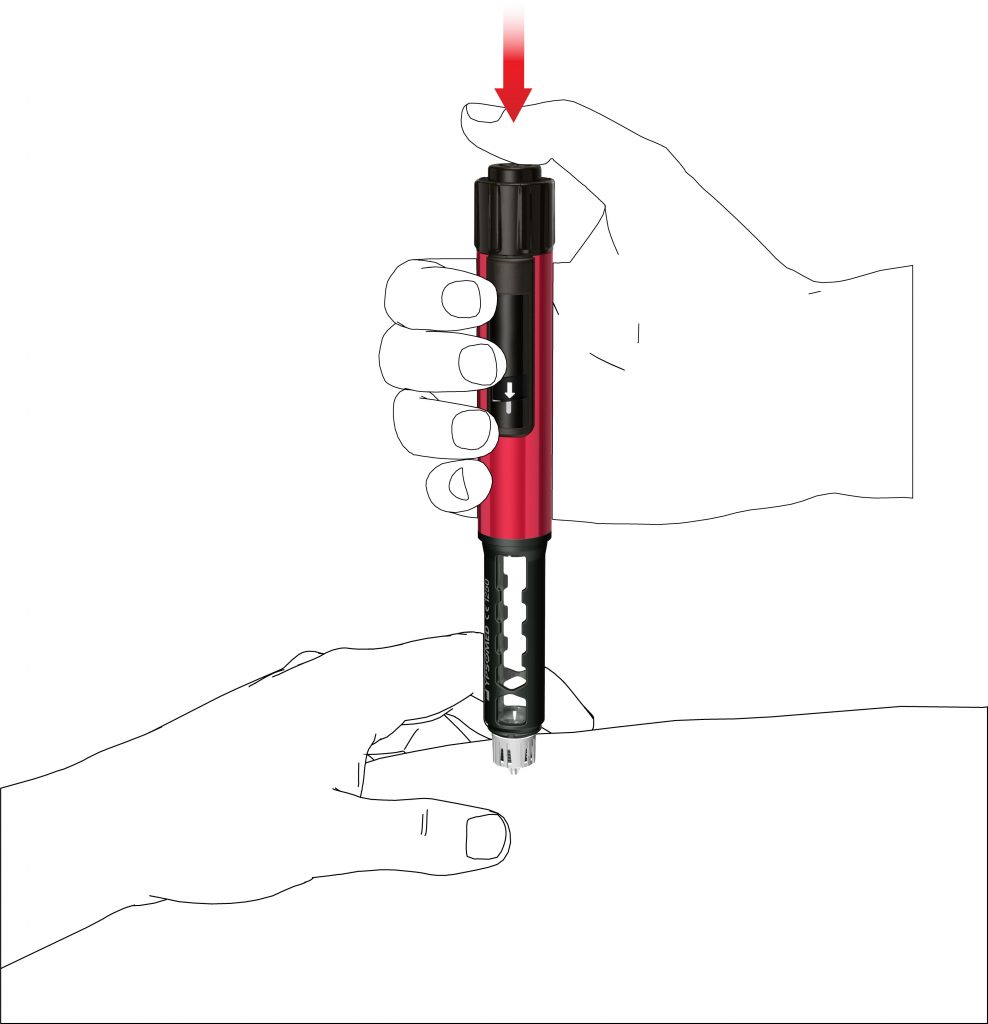
- Pull out the pen slowly. Check if the display is at the start position to make sure that the full dose has been injected.

3. Removing the pen needle
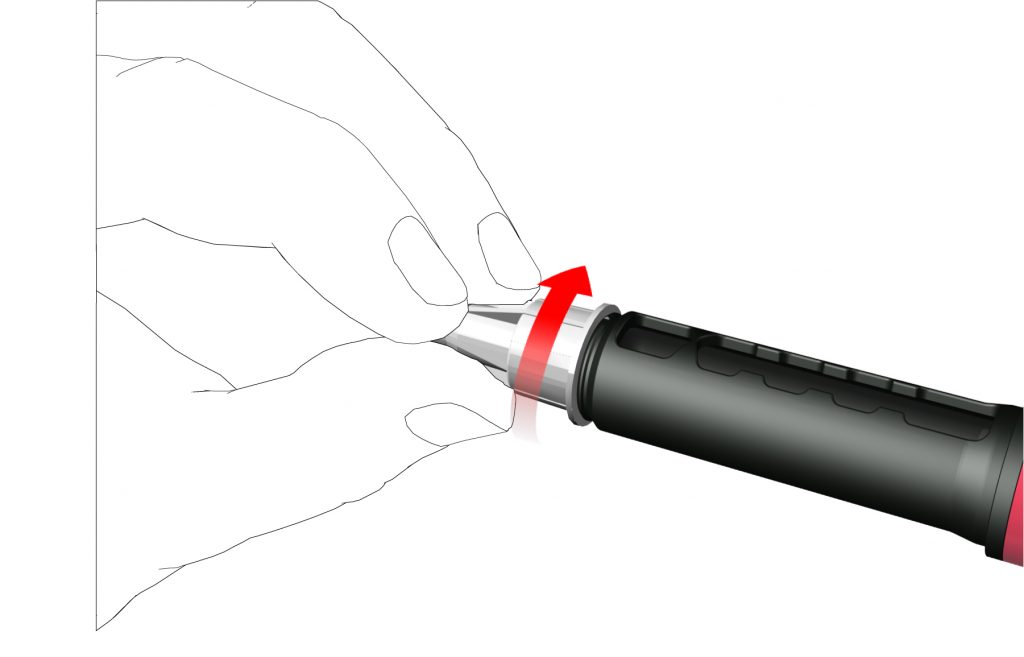
• Carefully attach the outer needle cap on the pen needle.
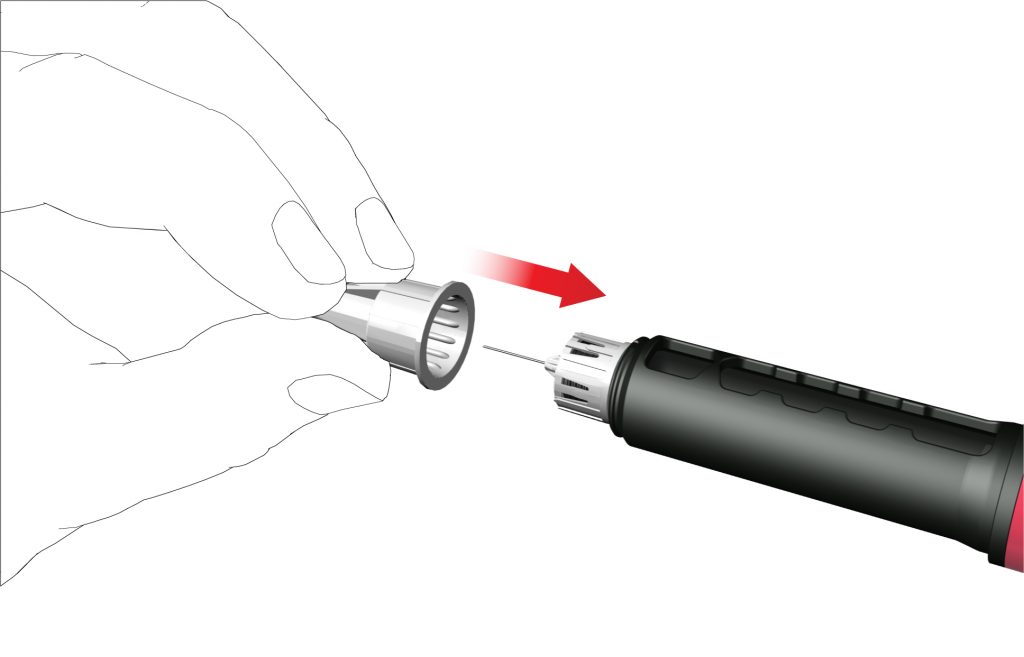
- Screw the needle cap anti-clockwise to remove the pen needle. Dispose of it correctly, for example, in a puncture-resistant sharps disposal container.
4. Re-attach pen cap
- Do not remove the cartridge from the Terrosa Pen before it is empty.
- Re-attach the pen cap after each use.
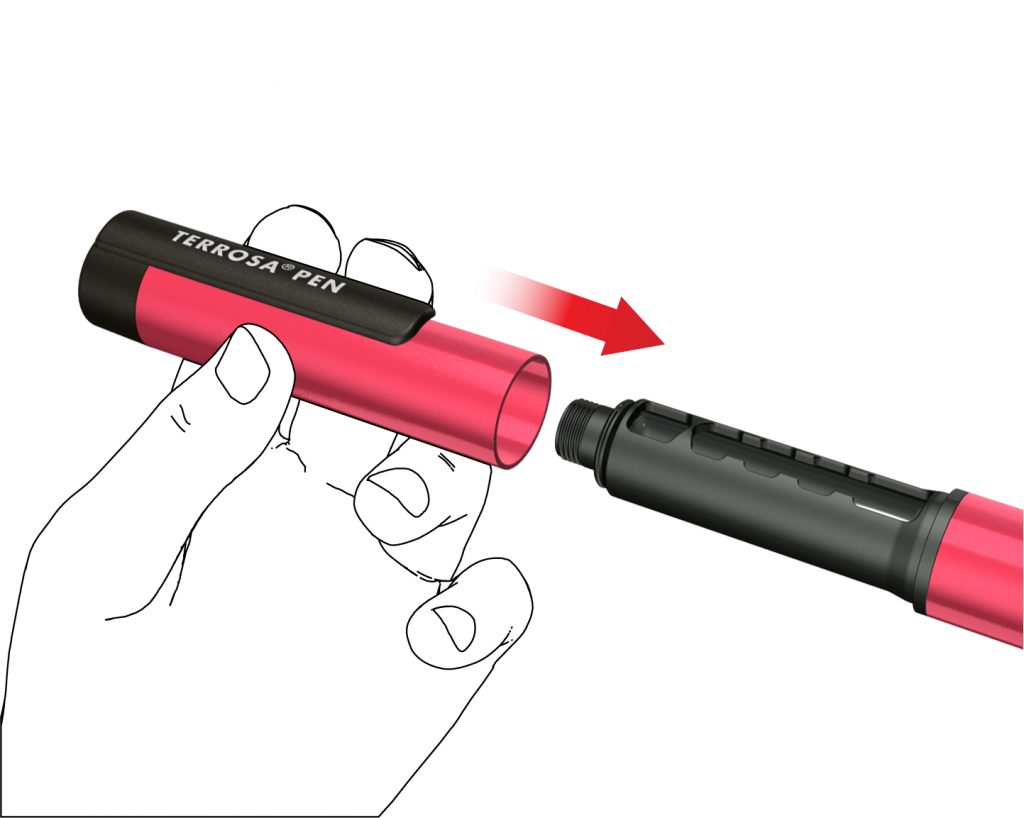
- Put the Terrosa Pen, with the cartridge inserted, back into the refrigerator between 2 and 8 °C immediately after use.
Note for healthcare professionals
Local, healthcare professional or institutional policies may replace the instructions regarding needle handling and disposal.
Additional information
The reusable fixed dose pen is designed for easy administration of Terrosa to treat osteoporosis. Each Terrosa cartridge contains 28 doses of fixed 80 microlitres Terrosa.
Use your Terrosa Pen only as prescribed by your doctor, in this instructions for use and the Terrosa package leaflet.
The Terrosa Pen can be used by self-injecting patients above the age of 18 years, healthcare professionals or third parties such as, for instance, adult relatives.
The Terrosa Pen must not be used by blind or visually impaired patients without help from a trained able-bodied person. Consult your doctor in the case of hearing or handling problems.
If you have any questions concerning the use of the Terrosa Pen, contact our customer service at any time.
telephone number: XXXXXXXXXXX
e-mail: XXXXXXXXXXX
Compatible pen needles
- Ypsomed mylifeClickfine 29 to 31 gauge (diameter 0.25 – 0.33 mm) and 12, 10, 8 or 6 mm length
- BD Micro-Fine Ultraneedles 29 to 31 gauge (diameter 0.25 – 0.33 mm) and 12.7, 8 or 5 mm length Pen needles from other manufacturers can be used according to their stated compatibility details. The pen needles must be used only once and the Terrosa cartridge must be used by one person only.
Storage and care of Terrosa Pen
- Handle your pen with care. Do not drop your pen and avoid knocking it against hard surfaces. Protect it from water, dust and moisture.
- A damp cloth is sufficient to clean the Terrosa Pen. Do not use alcohol, other solvents or cleaning agents. Never immerse the Terrosa Pen in water, as this could damage the pen.
- Do not use your Terrosa Pen if it is damaged or if you have any doubts about its correct functioning.
- Transport and store the Terrosa Pen with inserted cartridge at temperatures specified in the Terrosa package leaflet, provided separately.
- Store your Terrosa Pen, cartridges and pen needles out of reach of children.
- Do not store the Terrosa Pen with a needle attached as this may cause air bubbles to form in the cartridge.
Disposal of Terrosa Pen and used accessories
The Terrosa Pen has a service life of two years. Before disposing of the Terrosa Pen always remove the pen needle and the cartridge. Needles and used cartridges must be disposed of separately and safely. The Terrosa Pen can be disposed of according to the instructions of the local authorities.
Warnings
Follow the instructions presented in this instructions for use. If the instructions are not followed, there are risks of incorrect medication, inaccurate dosage, disease transmission or infection. Seek immediate medical advice if you have any health concern.
Warranty
The warranty covers manufacturing and material defects of your Terrosa Pen for two years of use, from purchase. It is limited to replacement of the pen. The warranty does not cover damages caused by:
- using cartridges other than Terrosa cartridges
- improper or careless use, handling or cleaning
- use contrary to the instructions for use
- the pen being used with a medical device, accessories or consumables other than those recommended by Gedeon Richter Plc.
- dropping, impact, application of force, contact with fluids
- other cases of exposure and wear, not in accordance with the instructions for use.
Troubleshooting
Follow the instructions given in the table if you have any questions regarding the use of Terrosa Pen:
| Question | Answer |
| 1. Small air bubbles are visible in the cartridge. | A small air bubble will not affect the dose, or harm. |
| 2. Needle cannot be attached. | Use another needle instead. Contact customer service if the second needle cannot be attached. |
| 3. Needle is broken/curved/kinked. | Use another needle instead. |
| 4. During dose dialling the pen does not provide an audible signal. | Do not use this pen; contact customer service. |
| 5. No medicine comes out of the needle during pen preparation step “G: Priming”. | Change the needle and repeat the priming as described in pen preparation sections “F” and “G”. If still no medicine is expelled, do not use this pen; contact customer service. |
| 6. The dose knob cannot be turned clockwise up to the arrow sign. | The amount of Terrosa left in the cartridge is less than 80 microlitres. Change the cartridge and the pen needle and perform priming according to the pen preparation. |
| 7. Display does not return to start position after injection. | Do not repeat the injection on the same day. Use a new needle for your injection on the following day. Set the dose and complete the injection as described in section “2. Setting the dose and injection”. If the display still does not return to start position after injection, do not use this pen; contact customer service. |
| 8. Spillage from pen is observed. | Do not use this pen; contact customer service. |
| 9. The dose knob inadvertently turned clockwise after completing the injection. How do I reset the dose knob to the start position? | Do not press the push button. Reset the pen by simply turning back the dose knob anti- clockwise to the start position. |
Legal manufacturer:
Ypsomed AG
Brunnmattstrasse 6
3401 Burgdorf, Switzerland
Video
This is an example page. It’s different from a blog post because it will stay in one place and will show up in your site navigation (in most themes). Most people start with an About page that introduces them to potential site visitors.

